An increasing number of companies are investing enthusiastically in chatbot solutions for a good reason. Thanks to technological advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and natural language processing (NLP), chatbots are more sophisticated than ever before. The chatbot market is projected to experience a staggering growth of 22.5% between 2020 and 2027, reaching a whopping $1,953.3 million by 2027.
In this guide, we’ll take a comprehensive look at the world of chatbots and gain a deeper understanding of how they can revolutionize the way we do business. The guide is divided into three chapters, each covering a different aspect of chatbots. In this first chapter, we will answer the question, “What is a chatbot?” and explain how they work. We will also explore their business use cases and benefits and how to choose the right chatbot for your specific needs. By the end of this chapter, you will have a solid understanding of the basics of chatbots to help you make an informed decision on implementing one in your business.
What is a chatbot?
A chatbot is a computer program capable of simulating human conversation through text or voice interactions. Chatbots are designed to automate and streamline communication between users and services. You can incorporate them into websites, mobile apps, messaging services, and virtual assistants for various functions like customer support, e-commerce, and information retrieval. In order to comprehend user inputs and reply to them, chatbots use machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP). They can be as basic as a rule-based chatbot system or as sophisticated as a conversational AI chatbot that offers tailored and situation-aware responses.
The history of chatbots
Chatbots have been around for a while, but quite recently, they have gained real popularity among users and businesses. The first chatbot ever was developed by MIT professor Joseph Weizenbaum in the 1960s, called ELIZA. It was the first machine capable of speech using natural language processing.
ELIZA made many people believe they were talking to a human by substituting their own words into scripts and feeding them with answers to maintain the conversation flow. Ever since the inception of chatbot technology with ELIZA, many more chatbots like PARRY (1972), Racter (1984), ALICE (1995), and newer voice chatbots like Siri (2010), Alexa (2015), and Cortana (2015) have been made. The chatbots got more conversational, better understood natural language, and became much more sophisticated with time.
However, the real revolution began when early in 2016, social media platforms like Facebook enabled developers to build a chatbot for their trademark or service. These messenger bots, widely used by companies worldwide today, allow customers to start a dialogue with a company by simply clicking on the messenger button. Enterprises have since used conversational AI applications worldwide to automate customer services and other organizational functions.
What are the types of chatbots?
Chatbots are widely classified into two types: rule-based and AI-based. Rule-based chatbots, as the name implies, reply to user input by following predetermined rules. AI-based chatbots, on the other hand, use machine learning and natural language processing to comprehend user input and respond accordingly.
Here are some examples of common types of chatbots and whether they are rule-based or AI-powered. It’s important to note that these distinctions are not always black and white and that some chatbots combine rule-based and AI-based methods.
Rule-based chatbots
Also known as flow-based or linguistic chatbots, rule-based chatbots use a tree-like flow to understand and solve customer queries. Instead of relying on complex AI algorithms, these chatbots are embedded with a set of predefined rules that they follow to understand and respond to customer inquiries. However, these chatbots have limited capability and can only answer specific questions.
While rule-based chatbots are less advanced than their AI-based counterparts, they are still valuable tools for businesses looking to automate basic and routine tasks. They can handle a high volume of customer interactions simultaneously, freeing your agents to focus on more complex issues. In short, rule-based chatbots can be a lifesaver for businesses looking for increased efficiency and labor cost reduction.
Keyword recognition-based chatbots
As the name suggests, these types of chatbots look for specific keywords in a customer’s query to present them with a suitable answer. Keyword recognition-based chatbots are an extension of rule-based chatbots and help answer repetitive or frequently asked questions (FAQs). They are often used for specific applications, such as customer service or e-commerce.
Menu-based chatbots
Menu-based chatbots, also called button-based chatbots, provide customers with a series of options to choose from in the form of menus and buttons. Depending on what the customer chooses, the chatbot then answers the question. They follow a predetermined path or a decision tree that helps them find the exact answer to a question. Menu-based chatbots are often used for simple tasks, such as ordering food or booking a flight.
AI-powered chatbots
AI-powered chatbots have a more sophisticated functionality and contextual awareness that require less training data than basic rule-based bots. They are built using powerful conversational AI technologies such as natural language processing and machine learning. These technologies enable them to understand the intent behind your questions, provide relevant responses in natural human language, and improve their performance over time with minimal or no human intervention.
Conversational AI enables AI-powered chatbots to provide a more personalized user experience with more fluid and direct conversations according to customer intent and sentiment. These experiences lead to more satisfied customers that are loyal to your brand.
Voice-enabled chatbots
Voice-enabled chatbots hear, perceive, and respond to your voice inputs via text, voice, or both by using NLP combined with speech-to-text (self-developed or already existing platforms). They are often used for hands-free user interactions, such as voice-controlled virtual assistants, and can be integrated into smart home devices or mobile apps.
Hybrid chatbots
These chatbots are built with a perfect blend of the simplicity of rule-based chatbots and the flexibility and intelligence of AI-powered chatbots. They initiate a conversation with the customer, ask them about their problem, record customer data, and then smoothly hand off the lead to a human agent.
Rule-based chatbots vs. AI-based chatbots
Chatbots powered by artificial intelligence (AI) are more sophisticated and adaptable than rule-based chatbots because they use natural language processing and machine learning to interpret and react to user inputs. This enables them to handle more complex jobs and respond in a more personalized manner.
Understanding the significant distinctions between rule-based and AI-based chatbots is crucial to selecting the ideal chatbot for your company’s needs and objectives.
Ability to understand user input: Rule-based chatbots can only interpret commands or specific phrases in established rules, limiting their natural language comprehension. On the other hand, AI-based chatbots can handle ambiguity and comprehend the context of the conversation, allowing them to comprehend and react to user inputs that have numerous meanings. They can comprehend varied inputs and offer more accurate and relevant solutions.
Ability to keep track of the conversation: Another big difference between rule-based and AI-based chatbots is that AI-based chatbots can keep track of the conversation as it goes in different directions. As a result, they can manage more complicated requests and respond in a more human-like manner. Rule-based chatbots cannot maintain context.
Ability to respond conversationally: Conversations with rule-based chatbots may feel robotic and monotonous because they can only give answers that have already been programmed. AI-powered chatbots can answer in a more human-like manner because they can comprehend the conversational context and respond accordingly.
Amount of maintenance required: The ease of the chatbot’s upkeep should also factor into your decision. Rules-based chatbot technology demands a lot of upkeep because you must manually implement any modifications to the rules or use cases. Conversely, AI-based chatbots require less upkeep because they can learn from user interactions and get better over time.
How do AI-based chatbots work?
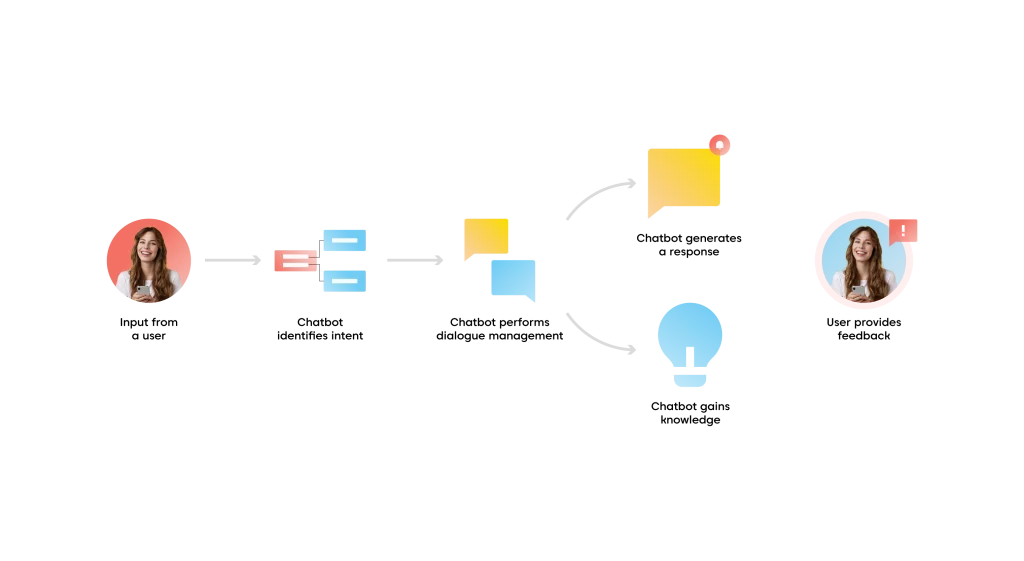
If you’ve read this far, then you know that artificial intelligence chatbots use natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) techniques to understand what users say and generate a reply. Here is a brief step-by-step overview of how a user’s exchange with an AI chatbot works:
Step 1: The user inputs a message:
To communicate with the chatbot, a user can type a message in text or record a voice message. The chatbot then receives the user input and processes it to understand the user’s intent.
Step 2: The chatbot identifies the user intent through NLP
The chatbot uses sophisticated NLP techniques such as parsing, part-of-speech tagging, named entity identification, and sentiment analysis to determine user intent. The chatbot uses the findings to determine the user’s intent and associates it with a predetermined action or reaction.
Step 3: The chatbot performs dialogue management
The chatbot uses dialogue management strategies to keep track of the discussion context and answer conversationally and naturally.
Step 4: The chatbot generates a response
Based on the conversation context and the intent, the AI chatbot responds.
Step 5: The chatbot gains knowledge through machine learning
AI chatbots employ machine learning algorithms to enhance their comprehension and responses gradually. They can gain knowledge from user interactions and apply this information to tailor interactions and boost efficiency.
Step 6: The user provides feedback on the interaction
The chatbot uses user feedback to enhance its comprehension and responses. Indirect or explicit feedback are both acceptable forms of this input.
What are chatbots used for?
AI chatbots are revolutionizing the way businesses operate across various industries. From providing customer service to streamlining internal processes, chatbots are becoming a go-to solution for many companies. Let’s take a look at some of the most common and popular use cases for chatbots:
Providing customer self-service: Chatbots can provide instant customer self-service around the clock. Chatbots can help scale customer support with limited agents for small businesses. For large enterprises, chatbots can help improve time to resolution and reduce the workload on human support agents. You can use chatbots to answer your customers’ FAQs, collect customer feedback, and more.
Providing personalized recommendations: Chatbots can engage your customers in conversations to collect information about their product preferences, past purchases, and browsing history. With this information, a chatbot can create personalized recommendations for product upsells or cross-selling your customers might be interested in.
Streamlining customer onboarding: Chatbots can help you provide an interactive onboarding experience tailored to each customer. Chatbots can help guide customers through your onboarding process, from helping them create an account to gathering information about your customer’s pain points and needs to recommend specific products or helpful resources.
Processing orders and refunds: Chatbots can guide customers through the checkout process, answer their questions about the product, and help them place an order. They can also provide quick updates on order status, including shipping and delivery information. When integrated with inventory and accounting systems, chatbots can even help process and handle refunds, which reduces errors, cuts labor costs, and improves efficiency.
Generating marketing and sales leads: Chatbots are excellent tools to help identify business leads from your website, messaging applications, or social media channels. Chatbots can engage visitors across digital channels and provide information about your company and its products or services to generate interest. They can also ask qualifying questions and collect contact information to help your sales team follow up and move them through your sales funnel.
These are just a few of the business use cases for AI Chatbots. For more chatbot use cases and real-life examples across healthcare, banking, education, and other industries, read Chapter 3.
Benefits of using chatbots
Improve customer experience and increase customer satisfaction
Implementing a chatbot on your digital channels can improve your customer experience by providing around-the-clock support with no wait times. Chatbots can promptly resolve customer queries and save them the time and effort of searching for answers by manually browsing your site or other online channels. Additionally, chatbots can provide a personal element to the customer experience, greeting customers by name and providing relevant responses based on customer history. These positive interactions with chatbots can improve customer satisfaction (CSAT) scores by up to 40% and improve customer loyalty to your brand.
Gain valuable customer insights and analytics
As chatbots interact with your customers daily, they collect data on each human interaction. This data can help you identify trends in common questions your customers have and help you improve your customer experience. Additionally, chatbots can give you insight into customer preferences and behaviors that can help you better understand customer needs and improve your products and services. You can also get a better idea of who your customers actually are and collect demographic information to run hyper-targeted marketing campaigns.
Reduce labor costs and improve productivity
Businesses can lower labor costs and increase operational efficiency by utilizing chatbots to handle simple customer service inquiries and freeing up human agents to address more complex requests. Additionally, chatbots can simultaneously serve several clients, answering more inquiries in a shorter amount of time than human agents. Businesses can enhance customer interaction without hiring additional employees by implementing AI chatbots. This ultimately leads to reduced labor costs.
Scale your customer support and provide 24/7 availability
Chatbots can manage several requests at once without needing extra agents or resources. In other words, a company can handle more client contacts without recruiting more customer service agents or shelling out more money. Additionally, chatbots work continuously without rest periods or interruptions, enabling your business to be accessible 24/7. Thanks to this, customers can use the chatbot at any time and get instant responses, whether your business is open or closed.
Streamline various business functions
Chatbots can be used for more than providing top-notch customer support. The ability to provide quick access to information and automate repetitive tasks can help capture sales leads, handle employee inquiries, schedule appointments, and track inventory, just to name a few examples. We will take a more in-depth look at some of these uses in the final chapter of the guide.
Grow your sales and revenue
According to business leaders, chatbots increase sales by an average of 67%. These intelligent virtual assistants identify opportunities for up-selling and cross-selling, make relevant recommendations, and help buyers throughout their journey, which can increase customer spending by almost 20% to 40%.
How to choose the best AI chatbot for your business
At this point, you might be wondering how to use all the information you’ve learned in this guide to choose the right chatbot solution for your business. Rest assured; we have put together a quick checklist of things you should consider to guarantee satisfaction with your choice.
1. Who is your target user?
The first step in choosing your chatbot is knowing who the end user will be. Create a customer persona to outline your typical customer’s needs, demographics, and behavioral information. Understanding the needs you need to fulfill will help you narrow down the features and functionalities your chatbot should have.
2. What are your goals for your chatbot?
Once you have a clear picture of who your chatbot will be for, you must identify the tasks you want your chatbot to handle. How can your chatbot provide value for your clients and enhance their experience? Thinking this through will help you determine the features your chatbot needs to reach your goals.
3. What digital channels do your customers use?
Chatbots can be implemented in numerous digital channels, including websites, mobile apps, social media, messaging platforms, and voice channels. It’s crucial to understand where your target user goes to look for information and where your chatbot would best serve your business objectives.
4. What features and capabilities are necessary to achieve your goals?
After compiling all the data from the earlier steps, you should have a decent notion of the features your chatbot needs to have. For instance, a simple menu-based chatbot could accommodate your expectations if you want your chatbot to gather details about a customer request before transferring them to a live person. In contrast, you’ll need an AI chatbot if you want it to gather user data to develop personalized customer experiences.
5. Do you want to create a chatbot from scratch or use a ready-made solution?
Though it can seem complicated, creating a chatbot is now simpler than ever. A team of skilled engineers had to be hired in the past, and creating a custom chatbot cost a considerable budget. Today, you can create your own chatbot tailored to your company’s requirements in a matter of minutes with the aid of a no-code chatbot builder.
Conclusion
We’ve covered a lot in this chapter, so let’s recap some key takeaways. We learned that a chatbot is a computer program that simulates human conversation using natural language processing and machine learning to interpret and react to user inputs. Chatbots have many applications, from automating customer support to streamlining internal HR processes. They can save businesses time and resources while offering users a more convenient and tailored experience. As technology advances, chatbots are growing increasingly more intelligent and are already capable of assisting humans over voice and other modern channels.
In the next chapter, we will walk you through how to build a chatbot and discuss what you need to consider before implementing this technology into your business workflow.
















